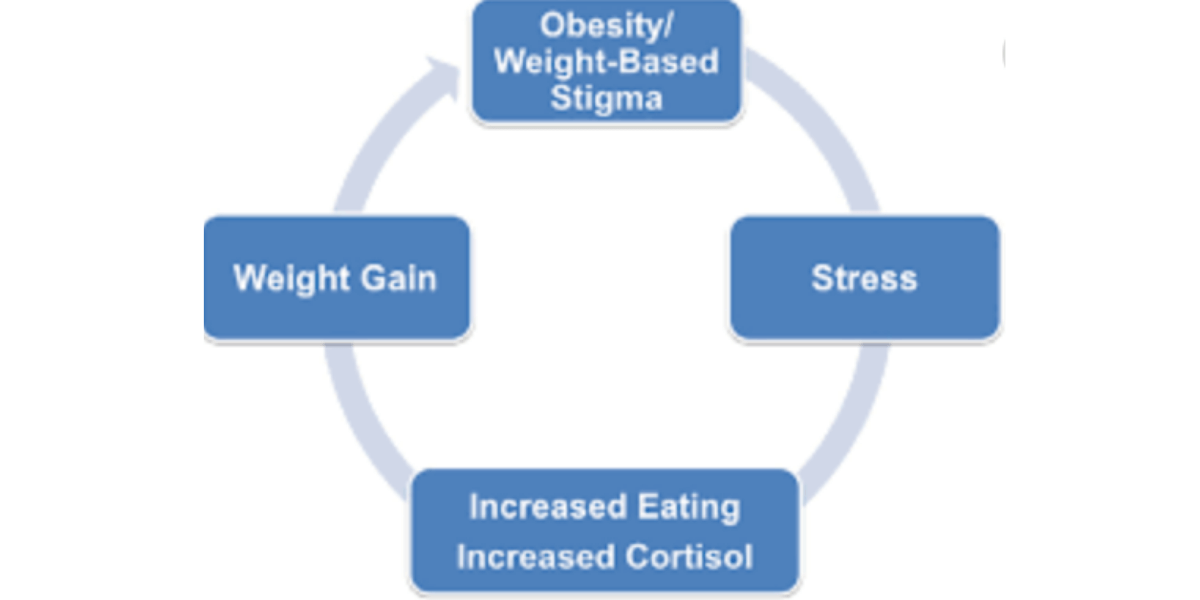
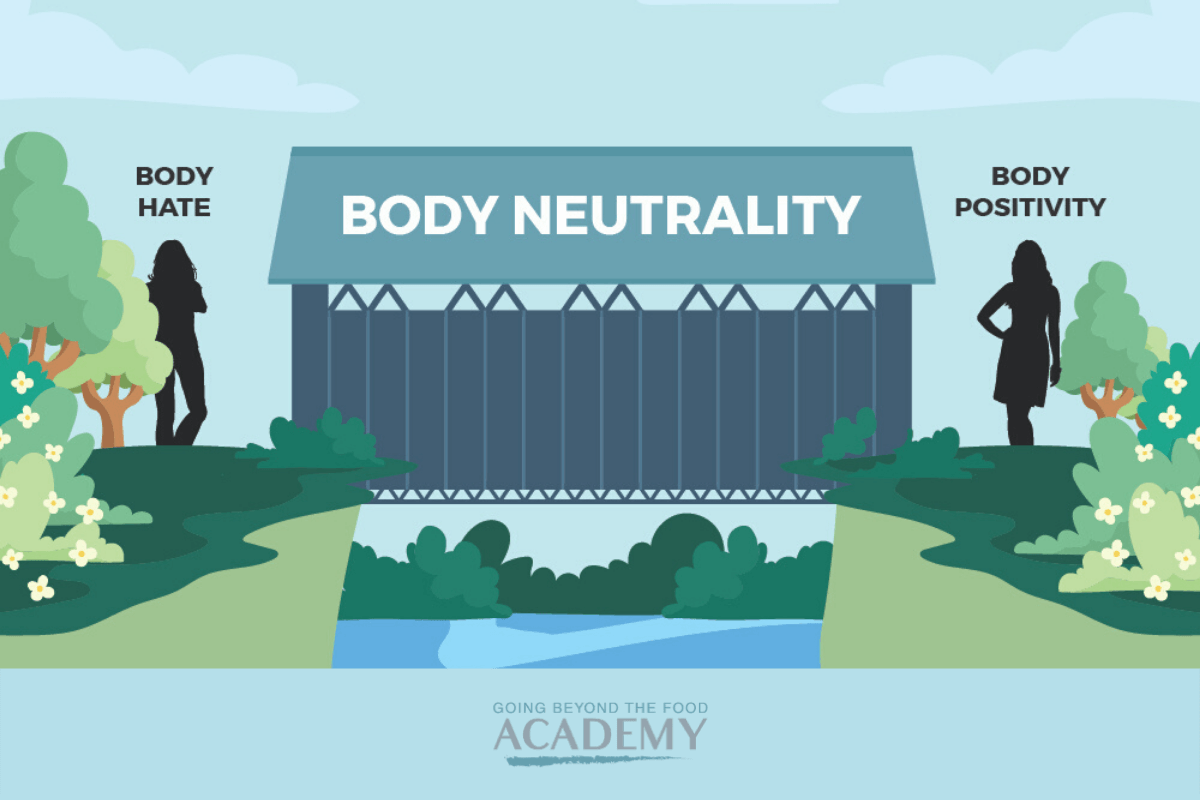
Do you feel trapped in an endless cycle of dieting, restrictive eating, and guilt? You’re not alone.
In this article, you’ll learn a compassionate, non-diet approach to developing a healthier relationship with food and your eating behaviors. Say goodbye to rigid rules and hello to sustainable strategies that align with your values and goals.
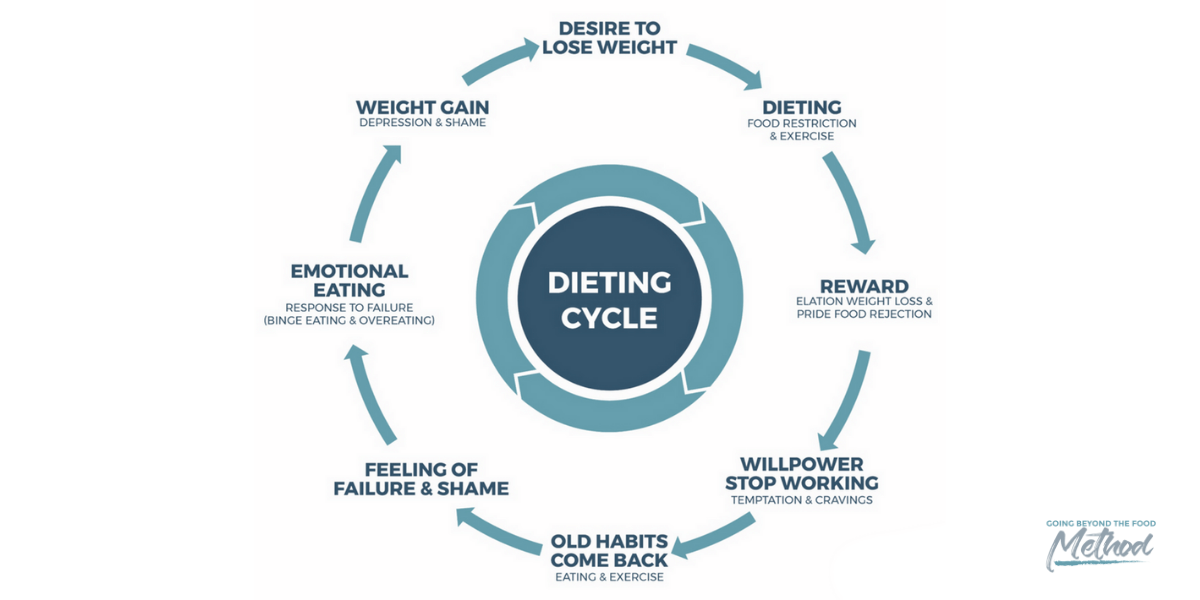
Many of us struggle with emotional eating, binge eating, or restrictive patterns that leave us feeling frustrated and disconnected from our true hunger cues. This vicious cycle can take a toll on our physical and emotional well-being, leading to feelings of shame, low self-esteem, and a preoccupation with food. But there is a way out – a path towards a more balanced, intuitive approach to eating.
Coaching Eating Behaviors: What to do instead?
The Cognitive Behavioral Coaching method enables you to explore your motivations, triggers, and patterns surrounding food. It helps cultivate self-awareness, mindfulness, and self-compassion, empowering you to make choices that truly nourish your mind, body, and soul. Prepare to break free from the diet mentality and embrace a healthier, more fulfilling way of living.
Instead of restrictive diets or one-size-fits-all rules, the CBC method encourages a more holistic and personalized approach to developing a healthy relationship with food. It’s about understanding your unique motivations, triggers, and patterns, and finding strategies that work for you – not against you.
Coaching Eating Behaviors Using CBC Coaching
The CBC approach is rooted in the principles of cognitive behavioral coaching, which recognizes that our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors are interconnected. By exploring and understanding these connections, we can identify areas for change and develop more constructive patterns.
Step 1: Understanding How Human Behavior is Generated
The first step in the CBC process is to gain insight into the fundamental drivers of human behavior. Our actions are influenced by a complex interplay of thoughts, emotions, physiological states, and environmental factors. By developing self-awareness and mindfulness, clients can begin to observe these influences without judgment, creating a foundation for lasting change.
Step 2: Investigate the Environment
Our physical and social environments play a significant role in shaping our eating behaviors. This step involves exploring the various cues, triggers, and situations that may contribute to unhealthy patterns. For example, a client may notice that they tend to overeat when stressed at work or when socializing with friends who encourage indulgence. By identifying these environmental factors, we can develop strategies to create a more supportive and conducive environment for healthier choices.
Coaching Eating Behaviors: 6 coaching questions
1. “What does a healthy relationship with food mean to you?”
This deceptively simple question encourages clients to reflect deeply on their values, priorities, and desired outcomes beyond just weight loss or adhering to food rules. A healthy relationship with food means different things to different people – it could mean feeling energized, nourishing their body with foods they enjoy, or setting an example of balance for their children. By defining what success looks like for them, clients can stay motivated and focused on their personal goals.
2. “How do your current eating behaviors align (or misalign) with your values and goals?”
Our actions often stem from deeply ingrained habits, emotions, or coping mechanisms that may no longer serve us. This question prompts clients to examine the alignment between their eating patterns and the things that truly matter to them. Perhaps emotional eating is causing feelings of guilt that conflict with their value of self-care. Or nighttime snacking might be hindering their goal of having more energy during the day. Exploring these disconnects can provide powerful motivation for change.
3. “What situations or emotions tend to trigger unhealthy eating patterns for you?”
Understanding personal triggers is crucial for interrupting unhealthy cycles. Clients may identify stress, boredom, loneliness, or even positive events like celebrations as common triggers for overeating or making poor food choices. Once these triggers are identified, we can co-create coping strategies and alternative behaviors to address them in a healthier way.
4. “How can you practice self-compassion when you experience setbacks or slip-ups?”
Change is rarely linear, and setbacks are an inevitable part of the process. This question encourages clients to treat themselves with kindness and understanding, rather than harsh self-criticism or shame. Self-compassion might involve reassuring self-talk, remembering that one lapse doesn’t undo all progress, or simply taking a moment to breathe and reset.
5. “What small, manageable steps can you take to move closer to your desired eating behaviors?”
Big, sweeping changes can often feel overwhelming and unsustainable. This question helps clients break down their goals into smaller, actionable steps that feel achievable. It could involve strategies like meal planning, trying new recipes, or finding alternative coping mechanisms for difficult emotions. Celebrating these small wins builds confidence and momentum.
6. “How can I best support and encourage you throughout this process?”
Every client is unique, with different needs, preferences, and circumstances. By asking this question, I ensure that my coaching approach is tailored to meet them where they are. Some may benefit from more accountability and structure, while others may need a softer, more self-compassionate style of support. Individualized coaching is key to lasting success.
Step 3: Show Why It’s Not About the Food
While food choices play a role, our relationship with eating often goes much deeper than what’s on our plate. This step involves exploring the underlying thoughts, beliefs, and emotional drivers that influence our behaviors around food. For some, food may serve as a coping mechanism for stress, loneliness, or difficult emotions. For others, deeply ingrained beliefs about body image, self-worth, or societal ideals may contribute to restrictive or binge eating patterns. By uncovering and addressing these root causes, we can begin to shift our relationship with food on a more profound level.
Step 4: Change the Thoughts/Beliefs
Once we’ve identified the unhelpful thoughts or beliefs driving unhealthy eating behaviors, the next step is to reframe and restructure these patterns of thinking. Cognitive-behavioral techniques, such as challenging cognitive distortions, reframing negative self-talk, and cultivating more compassionate inner dialogues, can be powerful tools in this process. For example, a client who believes they “don’t deserve” to eat certain foods might work on replacing that thought with a more balanced and self-accepting perspective. As our thoughts shift, so too can our behaviors and emotional responses to food.
Coaching Eating Behaviors: Key Takeaways
- Ditch the diets and embrace a kinder approach to eating that’s all about self-discovery, not self-denial.
- Get real with yourself about your motivations, triggers, and patterns around food so you can make choices that truly nourish your mind and body.
- Be your own bestie and practice self-compassion when you stumble – change is a journey, not a destination, and you’ve got this!
How we can help
You can access all of our services on our work with us page. We have a number of programs and service levels enabling us to serve most women:
Free Resources and Masterclasses: Get started and get to know us better!
Private coaching with Stephanie and her team Stephanie and her team of Certified Non-Diet Coaches are waiting to support you in a one-to-one setting with an individualized plan.
Undiet Your Life group coaching program is for women to learn how to eat intuitively, become body-neutral, and learn self-coaching at their own pace while being supported in a group setting by Stephanie and her team of Certified Non-Diet Coaches.